
Sistema endocannabinoide
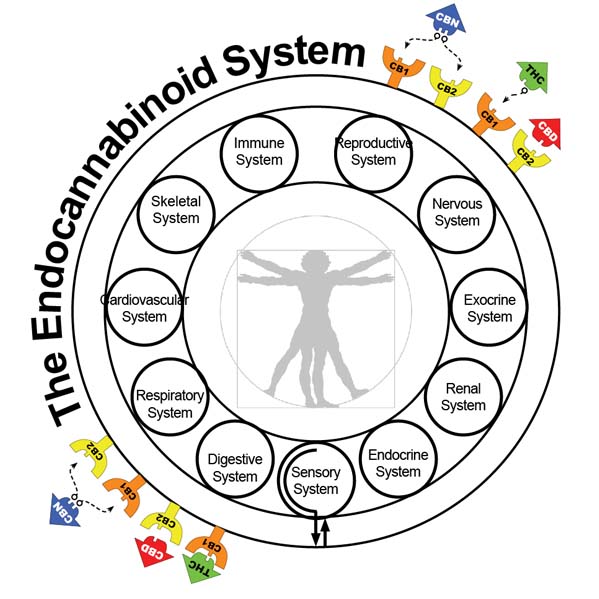
El sistema endocannabinoide (SEC) es un sistema biológico formado por neurotransmisores que se unen a los receptores cannabinoides, como CB1 y CB2, y a las proteínas receptoras de cannabinoides que se expresan en todo el sistema nervioso central (incluido el cerebro) y el sistema nervioso periférico.
Interviene en la regulación de los procesos fisiológicos y cognitivos, la actividad del sistema inmunitario, el apetito, la sensación de dolor, el estado de ánimo y la memoria, las funciones neuronales, incluido el control del movimiento y la coordinación motora, el aprendizaje y la memoria, la emoción y la motivación, el comportamiento similar a la adicción y la modulación del dolor, entre otros.
(245) 123 456
Descripción general del ECS
¿QUÉ ES EL CBN?
El CBN (cannabinol) es un fitocannabinoide no intoxicante que se encuentra en la planta Cannabis Sativa L.
¿QUÉ ES EL ECS?
El sistema endocannabinoide (SEC) es un sistema biológico formado por neurotransmisores que se unen a los receptores cannabinoides, como CB1 y CB2.
¿Qué son los receptores?
Son una clase de receptores que pertenecen a la superfamilia de receptores acoplados a proteína G. Son activados por endocannabinoides, que son producidos naturalmente por el cuerpo, o por fitocannabinoides.

¿Qué significa todo esto?
¿QUÉ ES EL CBN?
El cannabinol fue descubierto por primera vez en 1896 por Thomas Barlow Wood, W.T Newton Spivey y Thomas Easterfield. Es uno de los más de cien componentes del cannabis, que ha sido utilizado por personas y animales durante miles de años como alimento y para la salud.

WHAT IS THE ECS?
CBN regulates body processes, including sleep, pain sensation, mood, appetite, immune functions, brain plasticity, learning and memory, neuronal development, sensory system, inflammation, digestion, metabolism, energy balance, cellular system, and regulation of stress and emotions.
It is a complex system and it is clear that a lack of endocannabinoids are linked to a wide variety of illnesses.
What are receptors?
What is CAnnabis Sativa L.?
The plant has been used for thousands of years in cultures around the world. The scientific name is Cannabis Sativa L., and was named by Carl Linnaeus in 1753.
Recently, in the past hundred years, Cannabis has been greatly misunderstood and misrepresented. Before the laws and regulation, the plant has been used for many things in most of our cultures, including as food, clothing, medicinal preparations, fuel, and many other things. It has been used for close to 500 years in Mexico for material, food, material for ropes sails, books and clothing, as well as a medicinal plant for many ailments.

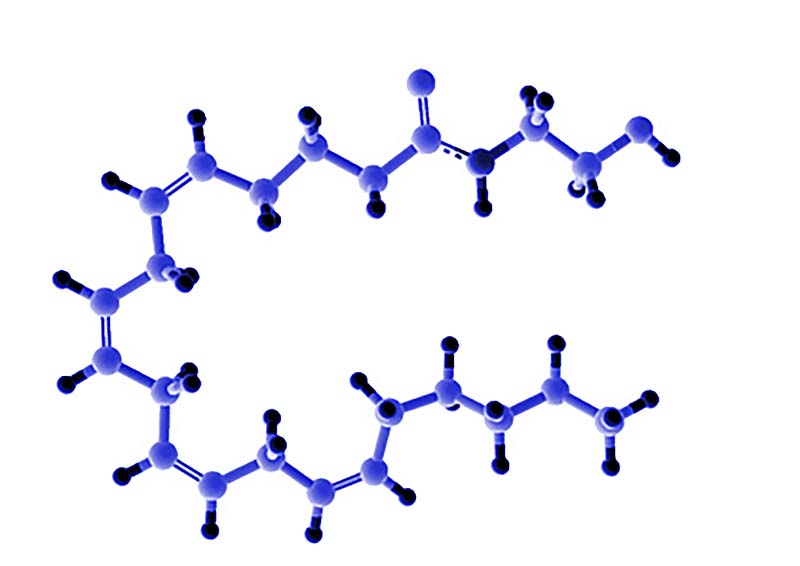
¿Qué son los endocannabinoides?
Los endocannabinoides se producen en nuestro cuerpo y son neurotransmisores capaces de enviar información de ida y vuelta. Se conectan a los receptores de cannabinoides, que son como puertas y como una computadora que envía información en ambos sentidos y obtiene más información para realizar un mejor programa. Estos incluyen anandamida y ácido araquidónico, que provienen del cuerpo y nos ayudan a lograr una mejor nutrición, fuerza, concentración y más.
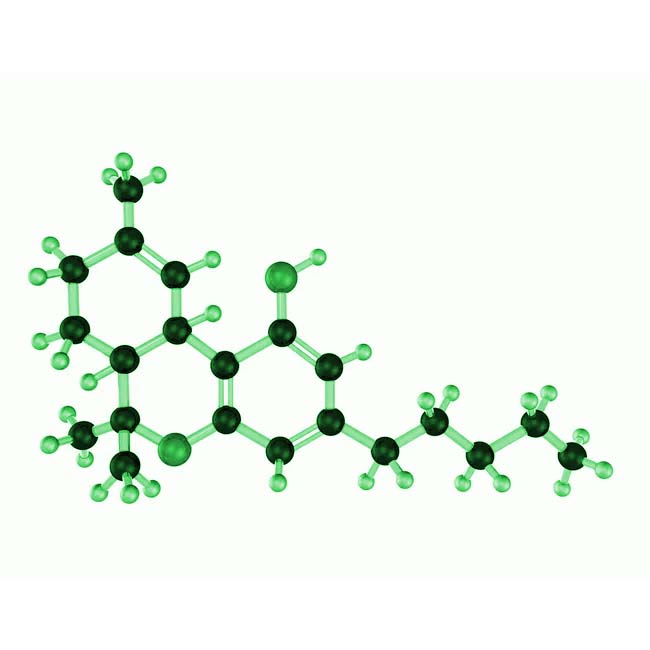
What are Phytocannabinoids?
Specifically, CBN is called Cannabinol, THC is known as Tetrahydrocannabinol, CBD is Cannabidiol, and CBG is Cannabigerol. There are dozens of others that are also present. These aid in our bodies ability to function at optimal levels.
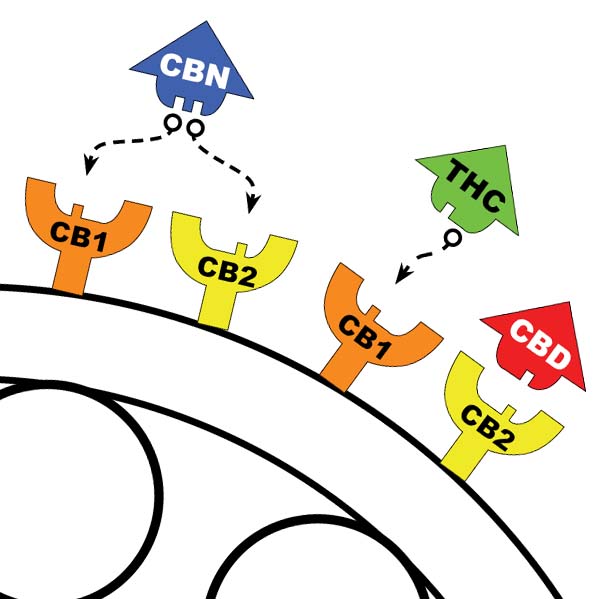
Cannabinoid Receptors in the body
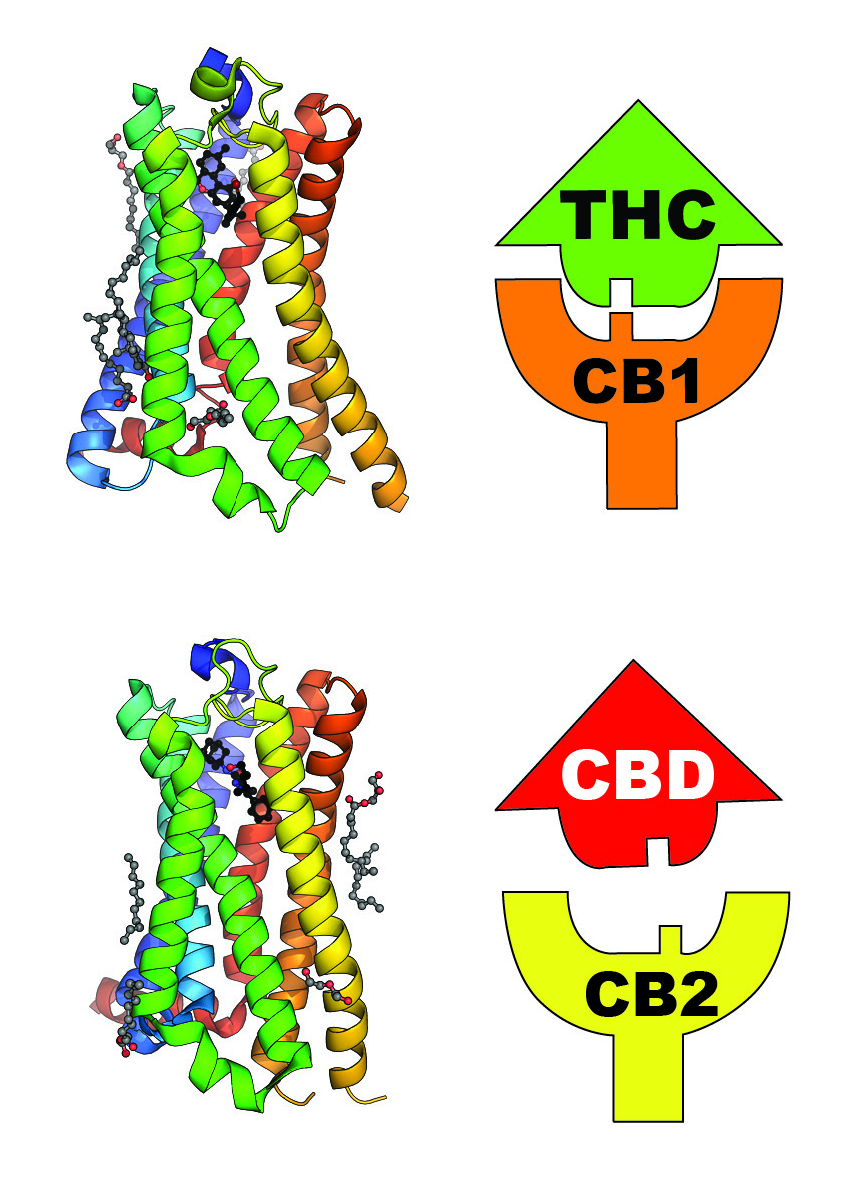
The CB1 receptor (also known as the cannabinoid receptor type 1) is a receptor that is abundant in neurons and plays a crucial role in regulating neurotransmission. It is primarily found in the central nervous system (CNS) and is activated by endocannabinoids, such as anandamide and 2-arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG), as well as by plant-derived phytocannabinoids like THC (tetrahydrocannabinol).
The CB1 receptor is involved in various physiological processes, including memory and learning, and has been connected to several diseases, including addiction, motor dysfunction, schizophrenia, and mood disorders such as depression and anxiety. It is also linked to various physiological processes, including pain modulation and inflammation.
CB2 receptor from the cannabinoid receptor family (the cannabinoid receptor 2) and is where the endocannabinoid 2-Arachidonoylglycerol (2-AG) connects. It is responsible for reducing or eliminating the psychoactive properties of the phytocannabinoid THC (tetrahydrocannabinol).
DETALLES
Intente utilizar plantas medicinales enteras en lugar de aislados. Esto se debe a la estabilidad de la naturaleza y al efecto séquito. El todo es mayor que la suma de las partes.

QUÉ ESPERAR DEL CANNABIS
Pricing & Plans
Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium.
Book Appointment
Sed ut perspiciatis unde omnis iste natus error sit voluptatem accusantium doloremque laudantium.
Contact Us
Call us

